There are three main types of graduate school student loans available: Federal Direct Student Loans, Federal Grad PLUS Loans, and Private Student Loans. Federal Direct Loans allow you to borrow up to $20,500 annually with a fixed interest rate of 4.3%. Grad PLUS Loans cover the full cost of attendance minus other aid, with a 5.3% interest rate. Private loans are offered by various lenders but typically require good credit and may have higher interest rates. Understanding these options is essential for your financial decisions; further details will help clarify your choices and their implications.
Federal Direct Student Loans
When it comes to financing your graduate education, Federal Direct Student Loans can be a valuable resource. Specifically, federal direct loans include unsubsidized student loans, which allow eligible graduate students to borrow up to $20,500 annually, with a total borrowing limit of $138,500. The interest rate for these loans is currently 4.3%.
Unlike other loans, federal direct loans don’t require a credit check for approval, making them accessible to a broader range of borrowers.
As you consider your options, it’s important to understand how interest rates compare to other types of loans and the total cost of borrowing. Interest accrues while you’re in school and during deferment, so planning is essential.
Fortunately, these graduate student loans offer flexible repayment options, including income-driven repayment plans that adjust your monthly payments based on your income level. This can greatly ease your financial burden after graduation.
Additionally, keep in mind that there’s an origination fee of 1.057% for loans disbursed between October 1, 2020, and October 1, 2021. With careful consideration, federal direct loans can help you achieve your educational goals without overwhelming financial strain.
Federal Grad PLUS Loans
When considering Federal Grad PLUS Loans, you need to be aware of the eligibility requirements and your repayment options.
These loans are designed specifically for graduate and professional students, allowing you to borrow up to the total cost of attendance minus any other financial aid.
Additionally, Grad PLUS Loans offer flexible repayment plans, including income-driven options, making it easier for you to manage your payments after graduation.
Eligibility Requirements
To qualify for Federal Grad PLUS Loans, graduate or professional students must be enrolled at least half-time in an eligible program at a participating school.
First, you need to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA), which helps determine your eligibility for federal financial aid, including these loans. Unlike other federal loans, Federal Grad PLUS Loans require a credit check. However, you can still qualify even if you don’t have an adverse credit history.
The maximum amount you can borrow through Grad PLUS Loans is equal to the total cost of attendance minus any other financial aid you receive. This means you can cover a significant portion of your educational expenses.
In addition, Grad PLUS Loans offer flexible repayment options, including income-driven repayment plans, making it easier to manage your payments after graduation.
It’s also important to note that you won’t be required to make any payments until six months after you leave school.
Repayment Options Available
Maneuvering repayment options for Federal Grad PLUS Loans can considerably impact your financial future. Typically, your repayment starts six months after graduation, giving you time to shift into the workforce.
When it comes to repayment plans, you have several options tailored to fit your financial situation. These include Standard, Graduated, Extended, and Income-Driven Repayment Plans, each designed to accommodate different needs.
The interest rates for Grad PLUS Loans are fixed at 5.3%, which, while higher than some federal student loans, can still be competitive with private loans. If you encounter financial hardships, you can take advantage of deferment or forbearance options, providing temporary relief from payments while you regroup or pursue further education.
Additionally, consolidating your Grad PLUS Loans into a Direct Consolidation Loan can simplify the repayment process. This option may allow you to extend your loan term, resulting in lower monthly payments.
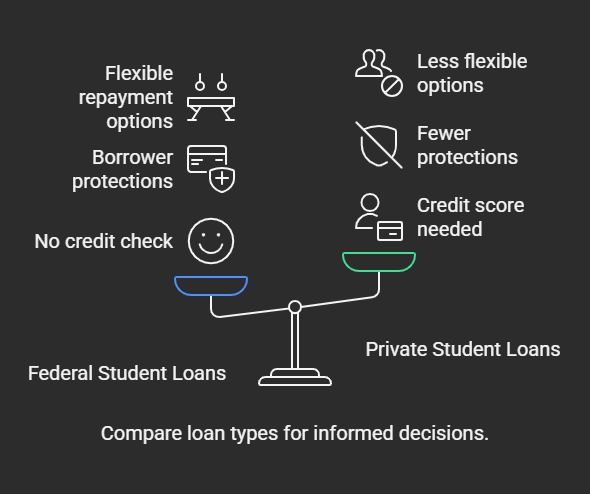
Private Student Loans
Many students consider private student loans as a viable option to finance their graduate education. These loans are offered by nonprofit and state-based lenders, often providing lower interest rates and no origination fees compared to federal loans.
To qualify for private student loans, you typically need good credit, often in the mid-600s or higher. If your credit history isn’t strong, a creditworthy co-signer can improve your chances of approval.
Private student loans usually feature fixed interest rates and may come with borrower benefits, such as principal reductions or flexible repayment options. You can tailor these loans to fit your financial needs, making them appealing for those looking to borrow for graduate studies.
However, it’s important to remember that private loans aren’t eligible for federal programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), so you should carefully consider long-term repayment options when borrowing.
For assistance in finding and comparing available private student loans that suit your financial situation, resources like ForYouNotForProfit.org can be invaluable. With the right information, you can make a well-informed decision about financing your graduate education.
Comparison of Loan Types
When considering how to finance your graduate education, it’s important to compare the different types of loans available, including types of auto loans. Graduate students use various loan options, including federal student loans and private graduate student loans.
Federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans allow you to borrow up to $20,500 annually, with an interest rate of 4.3%. These loans don’t require a credit check for approval, making them accessible for many.
On the other hand, Federal Grad PLUS Loans can cover your total cost of attendance minus other financial aid, with a higher interest rate of 5.3% and an origination fee of 4.228% for loans disbursed in the specified timeframe. These loans require a credit review for adverse history, which can be a hurdle for some.
Private loans, while potentially offering competitive interest rates and flexible repayment terms, typically require a minimum credit score in the mid-600s. They often lack the borrower protections that federal loans provide.
Additionally, repayment options for federal loans include income-driven plans, making them generally more flexible than private loans. It’s essential to weigh these factors carefully to determine the best loan type for your situation.
Loan Amounts and Limits
When considering graduate school, it’s important to understand the various loan amounts and limits you may encounter.
You can borrow up to $20,500 each year through Federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans, with a total cap of $138,500 for your graduate studies.
Additionally, Federal Grad PLUS Loans allow you to cover your entire cost of attendance, minus any other financial aid, providing a flexible option for funding your education.
Annual Borrowing Limits
Graduate students can borrow substantial amounts to finance their education, with federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans allowing up to $20,500 annually. This option is beneficial, as it provides a reliable source of funding for those pursuing an advanced degree.
Additionally, federal Grad PLUS Loans offer even more flexibility, allowing you to borrow up to the total cost of attendance minus any other financial aid you may receive. This means you could potentially cover all your educational expenses.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that borrowing limits can vary based on your enrollment status, whether you’re a full-time or part-time student, and the specific program of study you’re enrolled in.
Some graduate students may also look into private student loans, which can have markedly different borrowing limits. Certain lenders might even offer loans up to the full cost of attendance, which can exceed $100,000 for some programs.
Understanding these borrowing limits is vital, as they can directly impact your future repayment responsibilities. By combining federal and private loans, you’ll need to keep track of your total loan amounts to guarantee manageable repayment after graduation.
Total Loan Amounts
Understanding total loan amounts is vital for graduate students maneuvering through their financial options. When you’re considering federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans, you can borrow up to $20,500 annually, with a total borrowing limit of $138,500, including any undergraduate loans.
If you need to cover additional costs, federal Grad PLUS Loans are available, allowing you to borrow up to the cost of attendance minus any other financial aid received, without a specific annual cap.
For those pursuing high-cost programs like medical degrees, the maximum loan amounts can be considerably higher. Some lenders offer private student loans that can cover the remaining educational expenses, with some extending loans up to the full cost of attendance.
This can lead to total loan amounts reaching $350,000 or more, depending on your program and lender.
It’s important to understand these limits because borrowing beyond the maximum loan amounts can lead to financial strain after graduation. By being informed about your total loan amounts and limits, you can make better financial decisions as you pursue your graduate education.
Repayment Options
Maneuvering repayment options for student loans can be overwhelming, but knowing your choices makes a significant difference in managing your financial future.
Federal Direct Student Loans offer various repayment plans, including standard repayment, graduated repayment, and income-driven repayment options. These plans allow you to select a structure that best fits your financial situation.
For Grad PLUS Loans, you can defer payments for up to six months after graduation and even extend repayment up to 25 years with flexible repayment options.
When considering loans, remember that private lenders often provide less flexible repayment terms compared to federal loans. It’s essential to review their repayment structures carefully before making a commitment.
Federal loans also allow eligibility for income-driven repayment plans, which adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size, making it easier to manage payments.
Additionally, borrowers can take advantage of a 0.25% interest rate discount by enrolling in automatic payment plans for both federal and private loans. This helps reduce overall interest costs, making your student loan repayment process more manageable and affordable in the long run.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different types of graduate school student loans is essential for making informed financial decisions. Federal Direct Student Loans and Grad PLUS Loans offer various benefits, while private loans can provide additional funding options. It’s important to compare these options based on loan amounts, limits, and repayment plans to find what suits your needs best. By carefully evaluating your choices, you can better manage your education financing and set yourself up for future success.
Finance News 365 is an online platform dedicated to providing individuals and businesses with comprehensive financial insights, market trends, and resources to make informed decisions.







